Here some Basic Linux Commands which is used daily
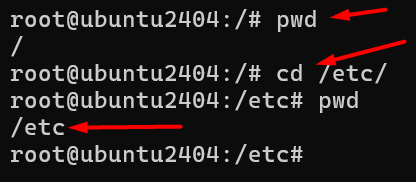
1 # pwd (Present /print working directory )
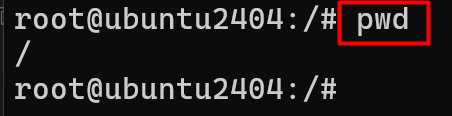
Shows your current folder location — useful to see where you are in the file system.
2 # ls (List Show )
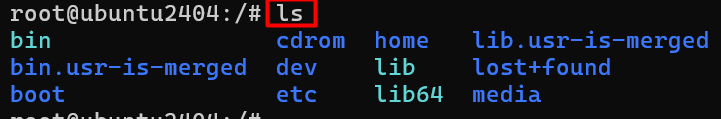
If you want show the file or folder insight the directory we can use ls command
3 # cd ( Change directory )
eg :- cd /etc/
If you want to move one place to other place one directory to other directory so we can use cd command
4 # mkdir ( Make directory )
eg :- mkdir linux
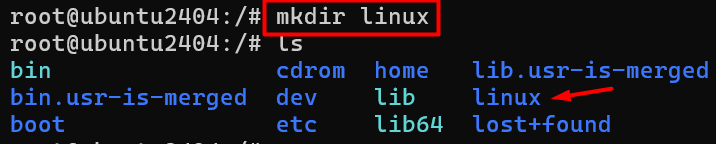
If you want to create a directory5
5 # rmdir ( remove directory )
eg:- rmdir linux
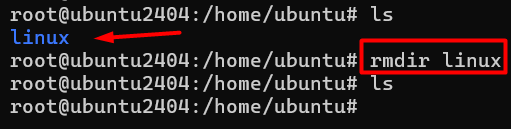
If you want to remove directory we use rmdir command
6 # touch ( create emty directory )
eg :- touch linux
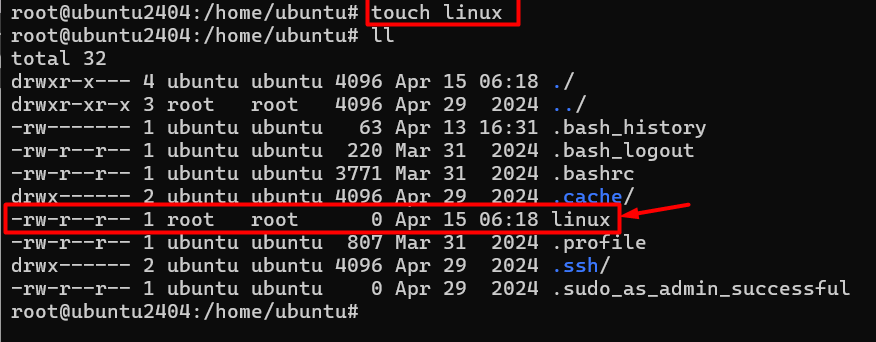
If you want to create empty file no data inside the file so we can use touch command
7 # rm (remove file )
Command :- rm (file name)
eg :- rm linux
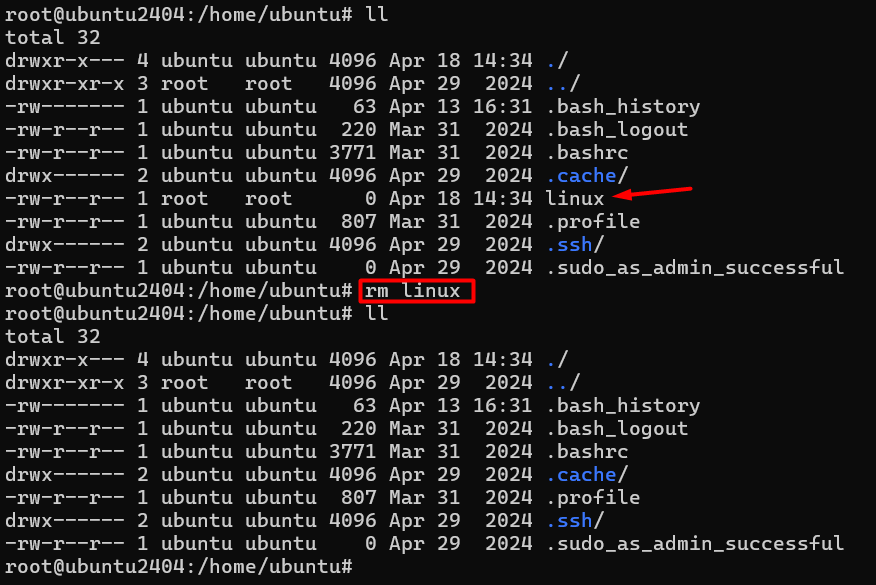
If you want a remove a file so we can use rm command.
8 # rm -rvf ( remove file or directory )
Command:- rm -rvf (file or dir name)
eg:-rm -rvf linux
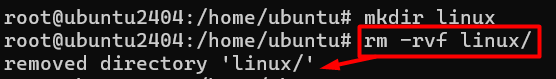
🔹 -r (or --recursive)
- Stands for: recursive
- Purpose: Tells
rmto delete directories and their contents recursively. - Without
-r,rmwill refuse to delete directories.
🔹 -v (or --verbose)
- Stands for: verbose
- Purpose: Makes
rmprint out details about what it’s doing — like the names of files and directories it’s removing. - Handy if you want to see exactly what’s being deleted.
🔹 -f (or --force)
- Stands for: force
- Purpose: Tells
rmto:- Ignore nonexistent files (no error messages)
- Never prompt for confirmation
- It forces deletion even if the file is write-protected.
So, rm -rvf does this:
Forcefully and recursively delete files/directories, while showing what’s being deleted.
Example:
rm -rvf my_folder
This will:
and show each deletion step as it happens.
delete my_folder and everything inside it,
not ask you “are you sure?” even for protected files,
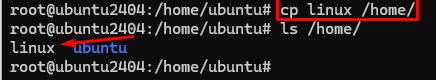
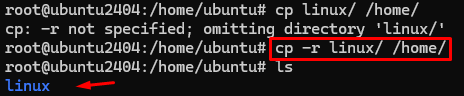
9 # cp ( copy file or directory )
Command :- cp (file name ) destination
eg:- cp
10 # mv ( Move or Rename)
Eg:- I have linux directory i want to reaname this one to ubuntu so i am use command bellow
#mv Linux ubuntu
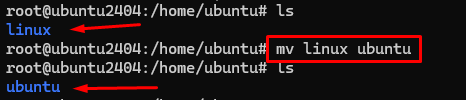
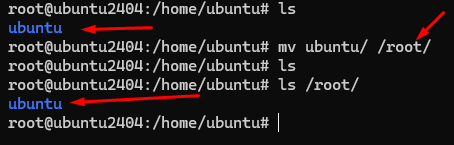
If you want move the ubuntu directory from /home to root directory
#mv ubuntu /root
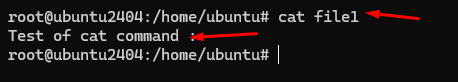
11 #cat (Concatenate and Display File Contents)
If you want to show the content of file then you need to use cat command
 Skip to content
Skip to content